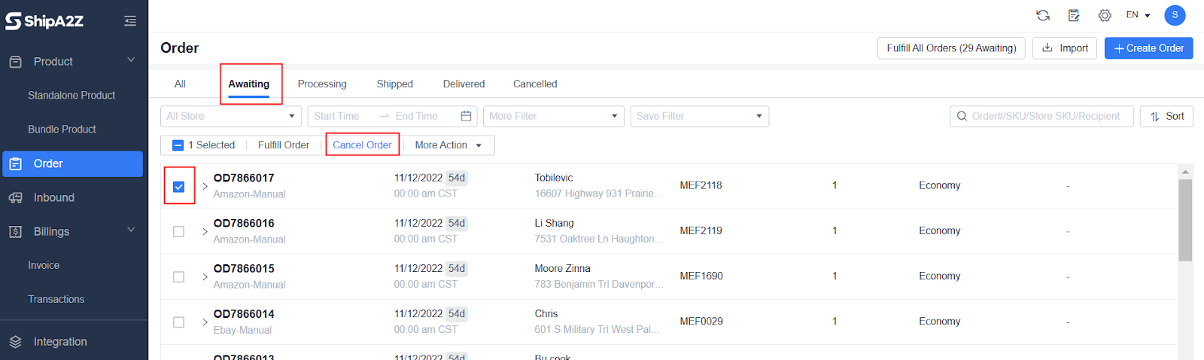
1. How to handle the situation if the buyer cancels the store order after the outbound order is submitted?
There are different ways to deal with different statuses of outbound orders.
(1) If it is in the status of “Awaiting”, the outbound order can be canceled without any impact on the inventory.
(2) If the order has proceeded to the other status, you need to verify with customer service whether it has been in transit.
- In-transit orders cannot be canceled directly.
- If the order status in the system is “Shipped”, but the package is still in the warehouse without being picked up by the carrier, you can communicate with customer service to intercept the package. In this situation, the outbound order can not be canceled in the system, you can contact customer service to cancel the shipping label offline and add back the inventory qty manually.
2. Can I modify the tracking number after it has been generated?
Yes.
OMS cannot modify the tracking number. You can only contact customer service to recreate the tracking number, but it can only be recreated before the product is shipped out.
3. Can I delete or modify the SKU after it is created?
The product name and SKU can be modified after creation. SKUs can be deleted if they have not been used (those not involved in any inbound or outbound process). Used products cannot be deleted.
4. Why can’t Amazon store products be processed in the system even after being mapped with an alias?
The Amazon product ASIN is unique. The Amazon store SKU pulled by ShipA2Z is an ASIN instead of an Amazon store SKU, so when the Amazon store product is mapped to an alias, the system SKU should be filled in with the ASIN instead of the Amazon platform SKU.
5. Must the SKU of the ShipOut system be the same as the SKU of the store?
When creating a product in the ShipA2Z system, the SKU can be set to be the same as or different from the store SKU. All products must be associated with the store SKU by mapping aliases after they are created in the system. After successful integration, the system can recognize the product regardless of whether the SKU of the system is the same as the SKU of the store.